The 12 Most Used Google Cloud Icons Explained!
Even if Google is one of the most organized companies in the world, trying to find the description of each GCP icon can still be a daunting task. Since Google Cloud architecture diagrams are a very important part of any cloud architect’s job, the Cloudockit team decided to assemble a list of the most important cloud diagrams used by Google Cloud Platform.
Please note that the information for the article was taken from various online sources. A full list of sources is available after the article if you wish to continue your research.
Virtual Machines

GCP Load Balancing icon
Load Balancing
The Google Cloud Load Balancer (GCLB) is a software-defined globally distributed load balancing service. It enables GCP users to distribute applications across the world and scale compute up and down with very little configuration and cost.

GCP Network Interface Card icon
Network Interface Card
A network interface card (NIC) is a hardware component, typically a circuit board or chip, which is installed on a computer so that it can connect to a network.

GCP VPC icon
Virtual Private Network (VPC)
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a global private isolated virtual network partition that provides managed networking functionality for your Google Cloud Platform (GCP) resources.

GCP VM icon
Virtual Machine Instance
An instance is a virtual machine (VM) hosted on Google’s infrastructure. You can create an instance by using the Google Cloud Console, the gcloud command-line tool, or the Compute Engine API.

GCP Persistent Disk icon
Persistent Disk
Google Persistent Disk is a durable and high-performance block storage for Google Cloud Platform. Persistent Disk provides SSD and HDD storage which can be attached to instances running in either Compute Engine or Google Kubernetes Engine.
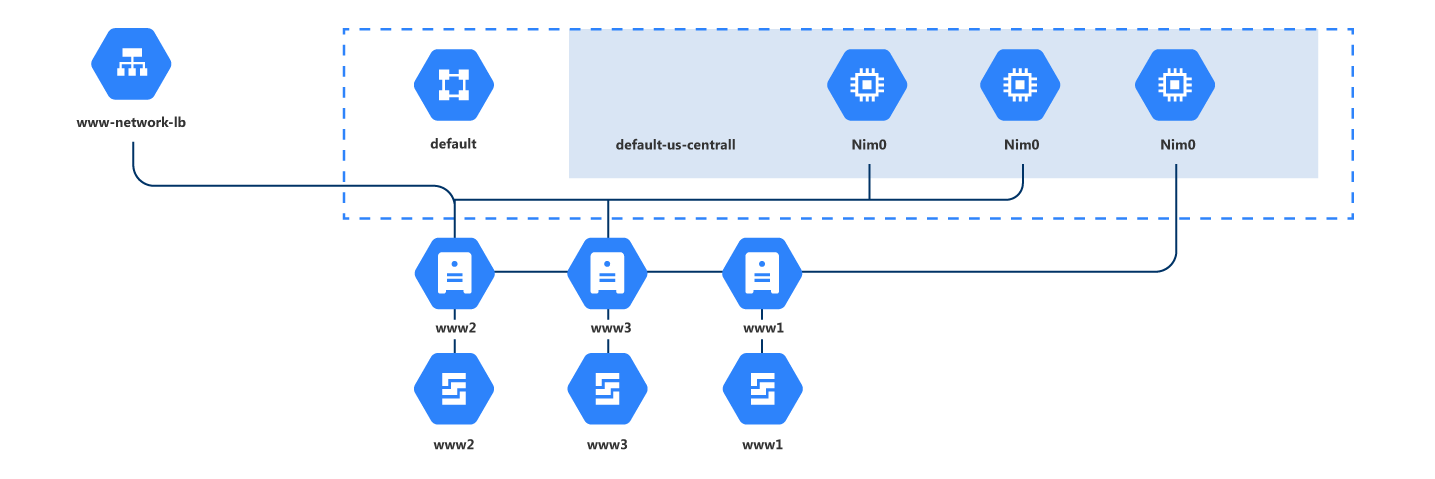
App Engines

GCP App Engine icon
App Engine
An App Engine app is made up of a single application resource that consists of one or more services. Each service can be configured to use different runtimes and to operate with different performance settings. Within each service, you deploy versions of that service. Each version then runs within one or more instances, depending on how much traffic you configured it to handle.

GCP App Engine Versions icon
App Engine Versions
Having multiple versions of your app within each service allows you to quickly switch between different versions of that app for rollbacks, testing, or other temporary events. You can route traffic to one or more specific versions of your app by migrating or splitting traffic.

GCP App Engine Services icon
App Engine Services
Use services in App Engine to factor your large apps into logical components that can securely share App Engine features and communicate with one another. Generally, your App Engine services behave like microservices. Therefore, you can run your whole app in a single service or you can design and deploy multiple services to run as a set of microservices.
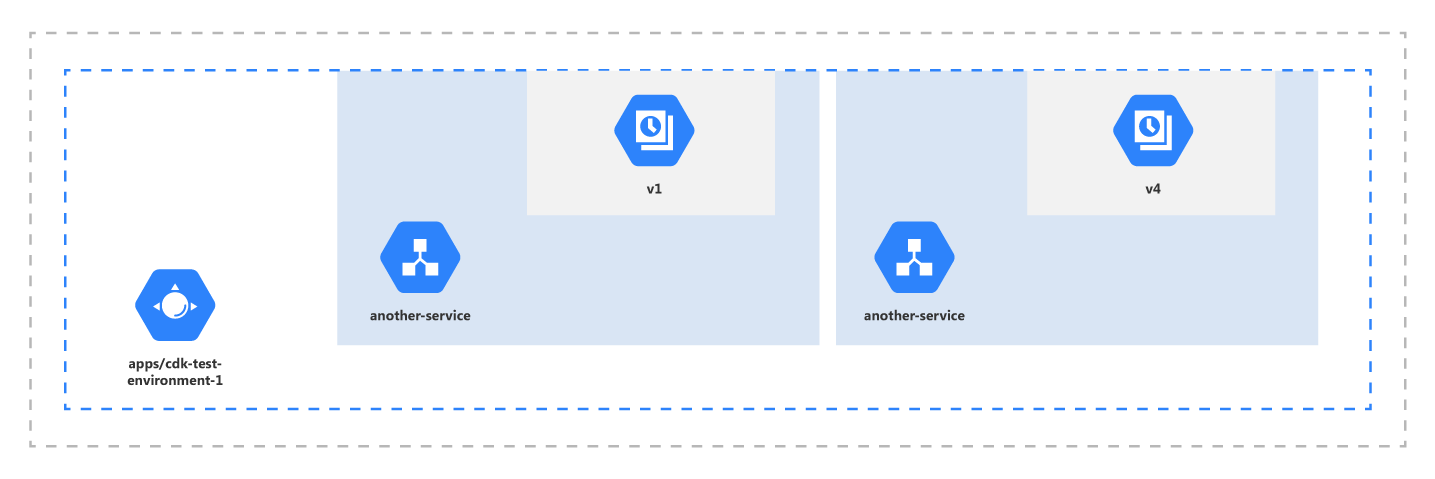
Cloud Formation

GCP Cloud Functions icon
Cloud Functions
Cloud Functions is Google Cloud’s event-driven serverless compute platform. Run your code locally or in the cloud without having to provision servers. Go from code to deploy with continuous delivery and monitoring tools.

GCP Buckets icon
Storage Buckets
Buckets are the basic containers that hold your data. Everything that you store in Cloud Storage must be contained in a bucket. You can use buckets to organize your data and control access to your data, but unlike directories and folders, you cannot nest buckets.
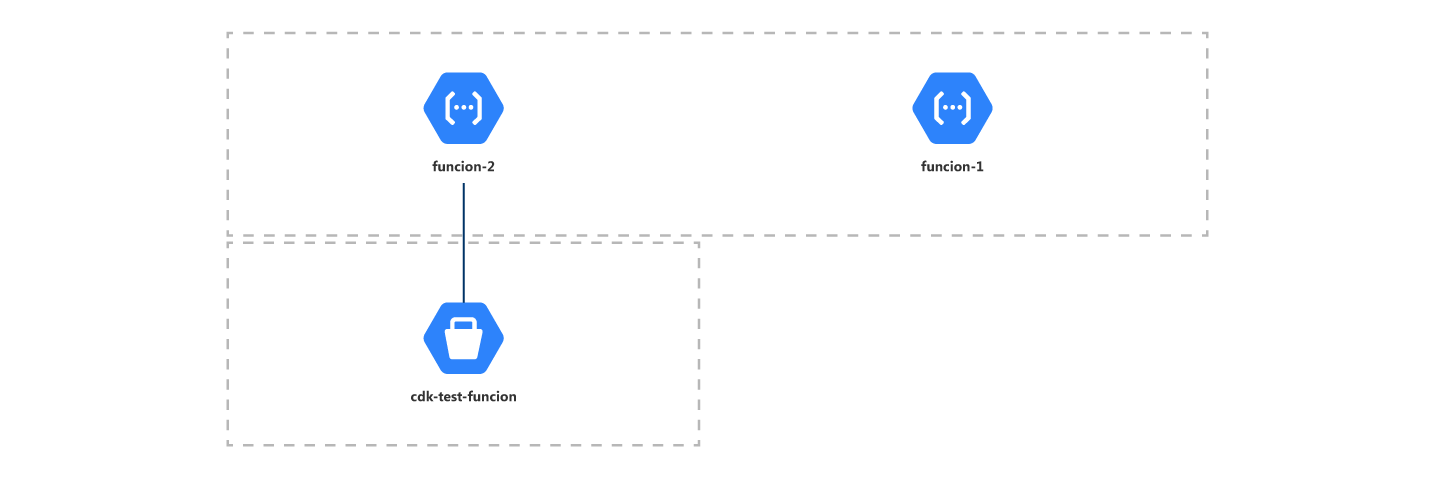
Other

GCP Route Tables icon
Route Tables
Google Cloud routes define the paths that network traffic takes from a virtual machine (VM) instance to other destinations. These destinations can be inside your Google Cloud Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network (for example, in another VM) or outside.
GCP Resources icon
Resources
GCP consists of a set of physical assets, such as computers and hard disk drives, and virtual resources, such as virtual machines (VMs), that are contained in Google’s data centers around the globe.
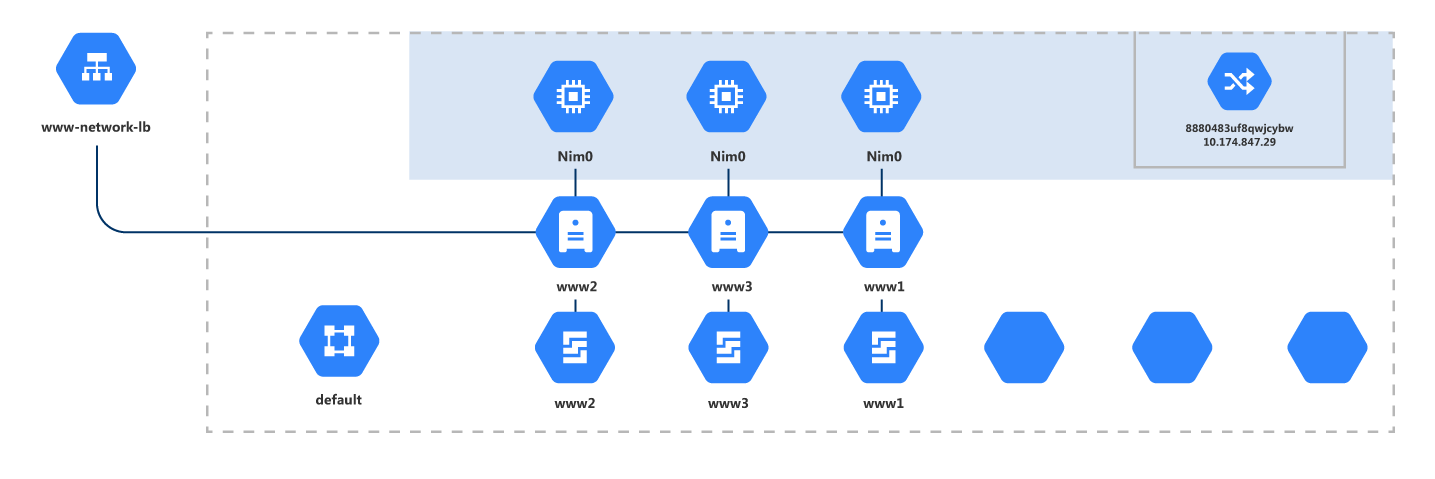
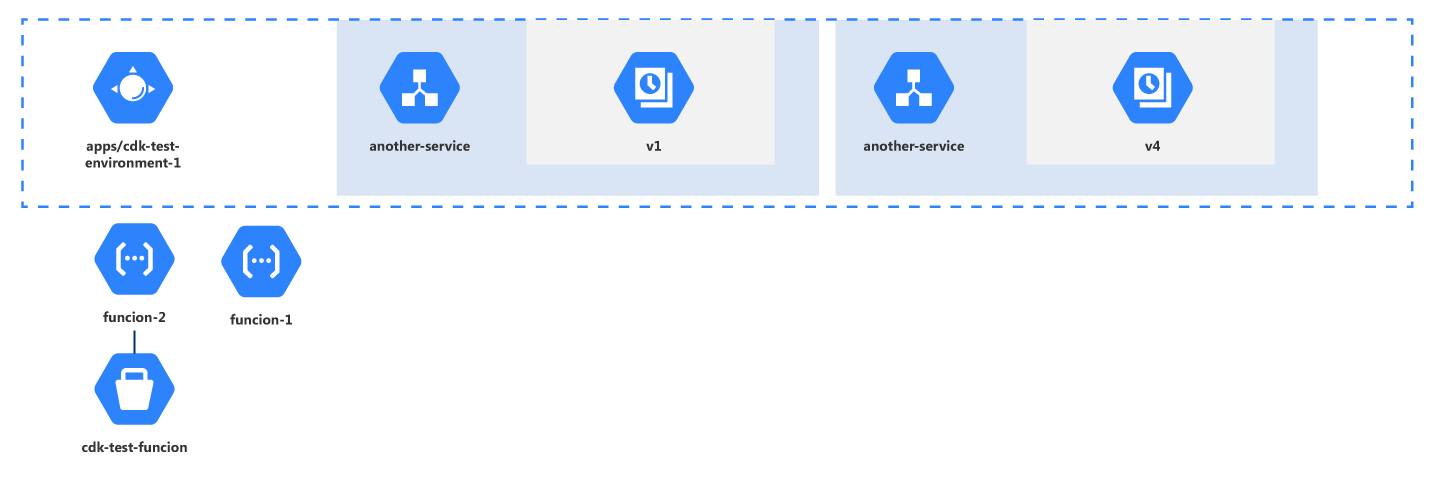
Cloudockit’s Google Cloud Architecture Diagram Tool
Cloudockit is currently the only Google Cloud architecture diagram tool available on the market today. With this diagram tool, you will be able to view your cloud diagrams in 2D or 3D and even schedule the generations so you never forget the updates. Constant monitoring of your cloud is key to having a secure cloud environment!
Sources
App Engine / services / versions: https://cloud.google.com/appengine/docs/standard/python/an-overview-of-app-engine
Cloud Functions: https://cloud.google.com/functions
Load Balancing: https://medium.com/google-cloud/google-cloud-load-balancer-setup-tweaking-and-observations-c12d704e6d52
Network interface card: https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/network-interface-card
Persistent Disk: https://cloud.google.com/persistent-disk
Ressources: https://cloud.google.com/docs/overview
Route Tables: https://cloud.google.com/vpc/docs/routes
Storage Buckets: https://cloud.google.com/storage/docs/key-terms
Virtual Machine Instance: https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/instances
VPC Network: https://www.networkmanagementsoftware.com/google-cloud-platform-gcp-networking-fundamentals/
Previous Post