Knowledge Base
MSP – Azure
Introduction
The purpose of this document is to provide the detailed steps to install and configure Cloudockit Desktop in an optimal way so you can get going as quickly as possible with your automated documentation generation for your Azure environment.
Cloudockit desktop can be installed in many ways. On a workstation, on a server, or on a virtual machine.
Based on our experience, we have identified that the optimal way is to create a virtual machine using the image available on Azure Marketplace which includes Cloudockit Desktop.
Step 1 – Creating the virtual machine
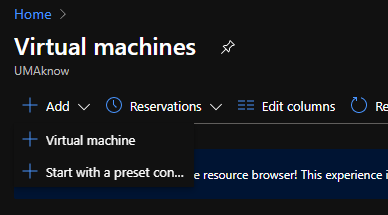
Connect to the Azure portal and go to Virtual Machines
From the Virtual Machines page, click on Add in the upper left corner and then Virtual Machine.
BASICS
Project Details
Add the Virtual Machine to the Resource Group of your choice.
Instance Details
- Virtual Machine Name: Name your virtual machine
- Region: Select Region
- Availability options: Select from the drop-down.

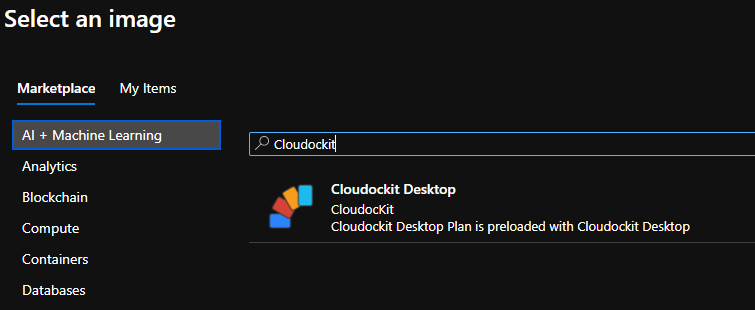
Click on Browse all public and private images
In Select an image, enter Cloudockit in the search bar and select Cloudockit Desktop.
Azure Spot Instance: No
Size: Standard_A2_v2 – 2vcpus, 4 GiB memory (Suggested)
Administrator Account
Define the Username and Password
Inbound port rules
Public Inbound ports: Allow selected ports
Select Inbound ports: RDP (3389)
Licensing
Would you like to use an existing Windows Server license? Based on your own preferences.
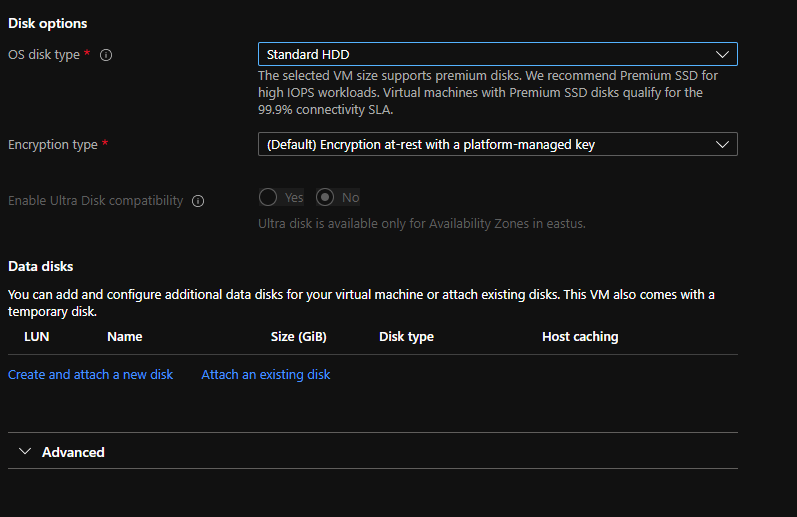
Click on Disk
DISKS
Click on Networking
NETWORKING
Network Interface
Define the configuration as shown in the image below.
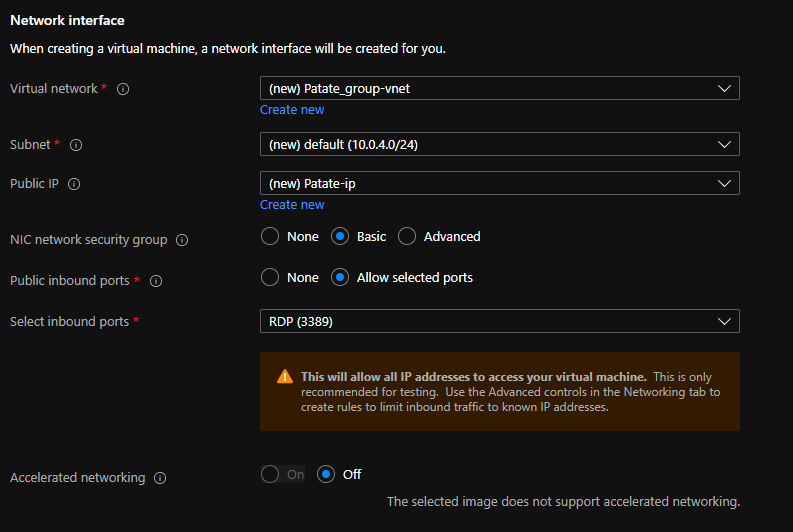
Load Balancing
Do you want to place this virtual machine behind an existing load balancing solution?: No
Click on Management
MANAGEMENT
Define Management as shown in the image below.
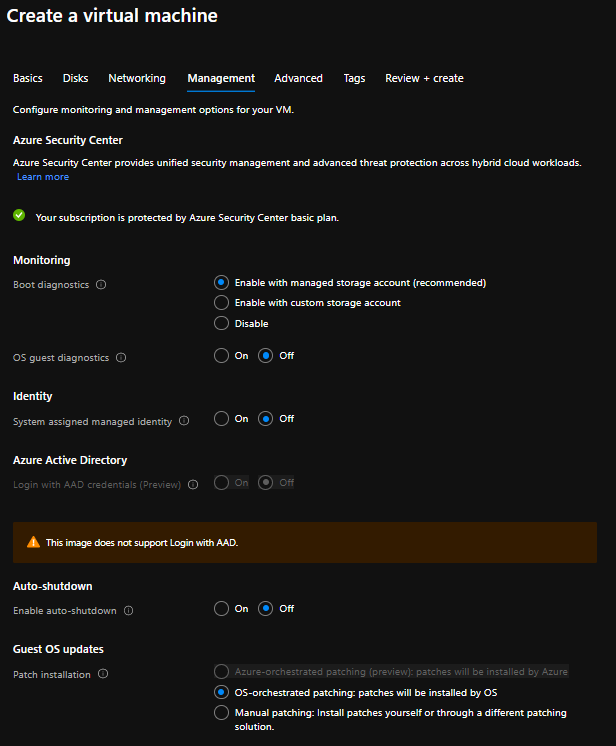
Click on Advanced
ADVANCE
Define the Advanced tab as shown in the image below.
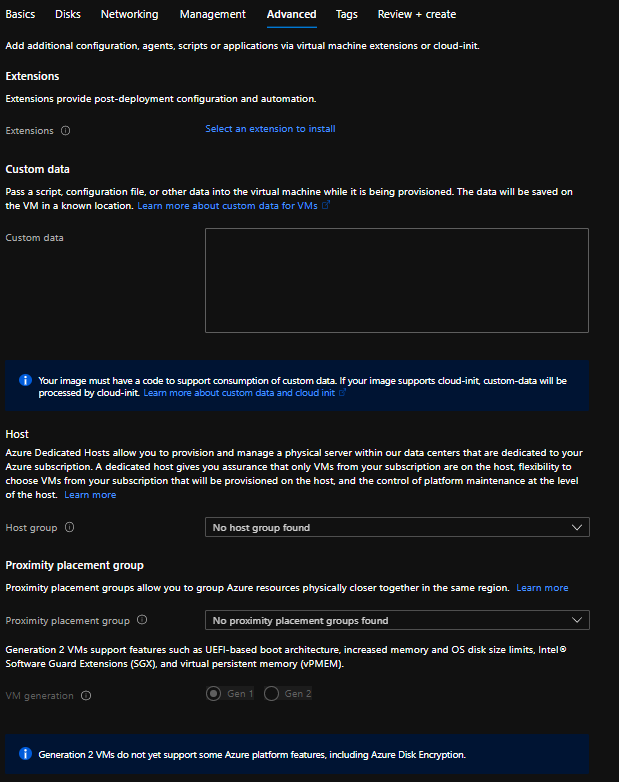
Click on Tags
TAGS
Define tags based on your organization’s tagging policy.
Click on Review + Create
REVIEW & CREATE
Review the parameters of the virtual machine and click on Create.
Step 2 – Creating the Storage Account
The Storage Account will allow you to save the documentation that you create and be available to employees in your organization.
From the Azure Portal, select Storage Accounts
Click on Add in the upper left corner.
BASICS
Define the Basics section as shown in the image below.
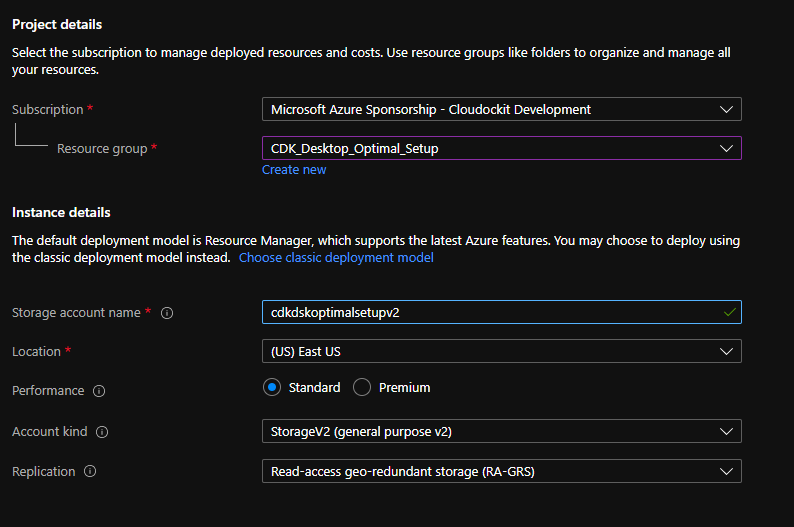
Click on Networking
NETWORKING
Define the Networking based on your organizations’ policies.
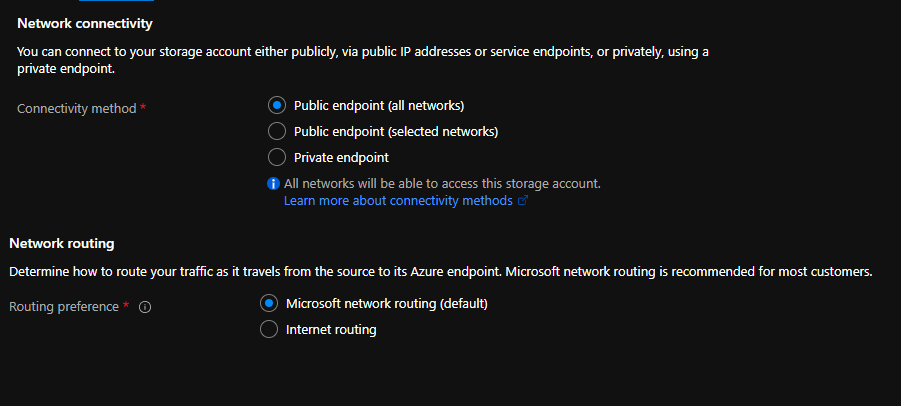
Click on Data Protection
DATA PROTECTION
Define the Data Protection based on your organization’s policies.
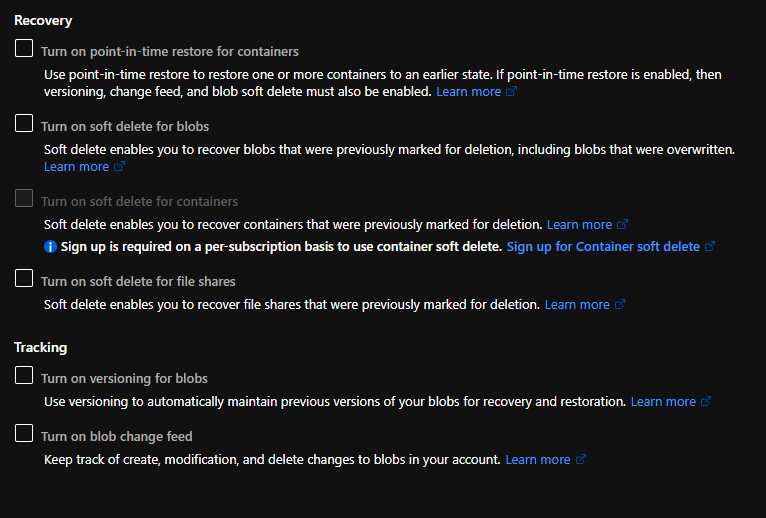
Click on Advanced
ADVANCE
Define the Advanced tab as shown in the image below or based on your organization’s policies.
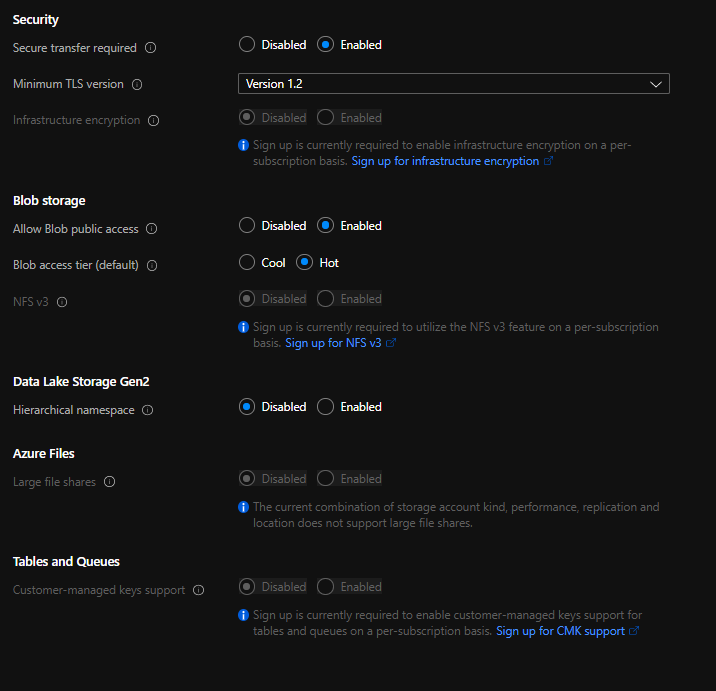
Click on Tags
TAGS
Define Tags based on your organization’s tagging policy.
Click on Review & Create
REVIEW & CREATE
Review the parameters of the virtual machine and click on Create.
Step 3 – Creating an App Registration
Your customer can create an app registration on their tenant and share these credentials to allow you to connect to their subscription and generate documentation on their cloud infrastructure.
CREATING AN APP REGISTRATION
- Connect to your Azure Portal
- Select Active Directory
- From the menu, select App Registrations
Click on New Registration
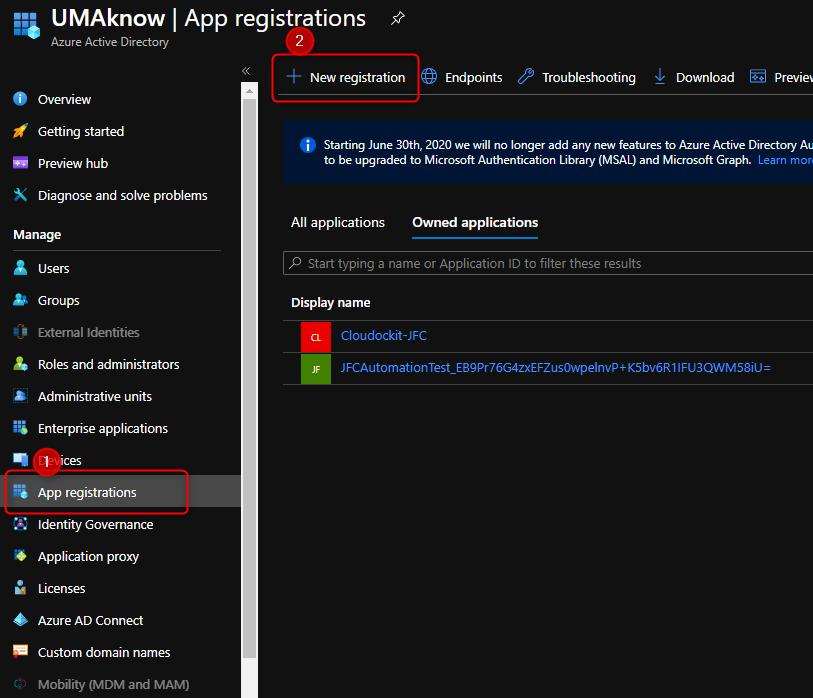
Enter the unique name of your application.
Click: Register
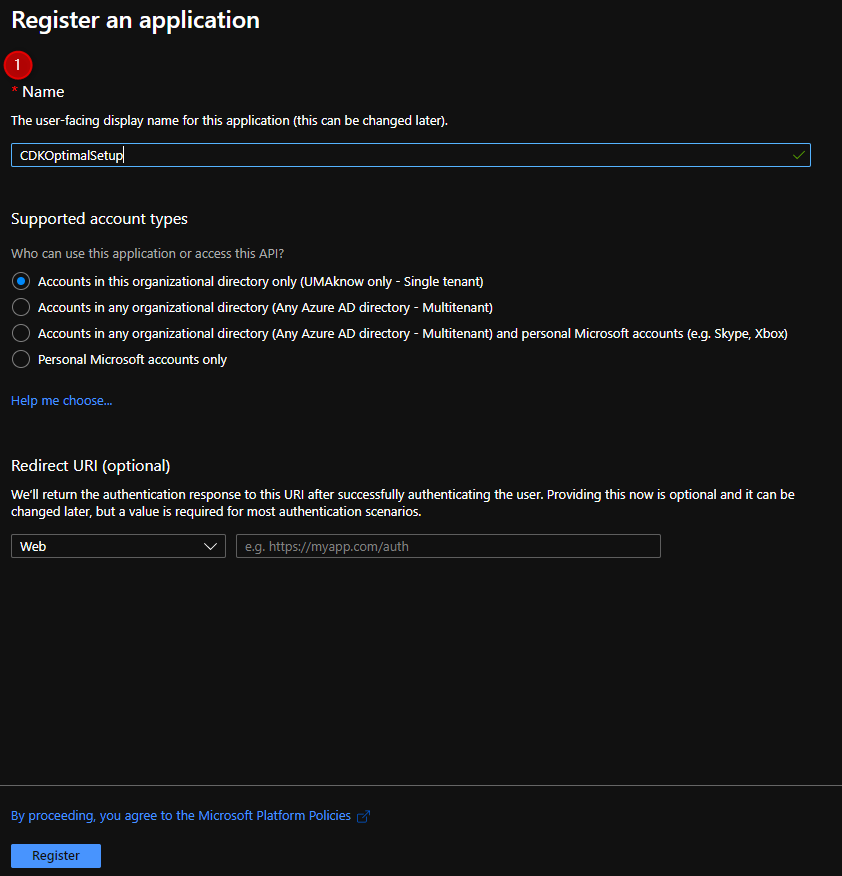
Save the Application and Directory ID.
CREATING AN APP SECRET
From within the Application
Click on Certificated and Secrets
Click on New client secret
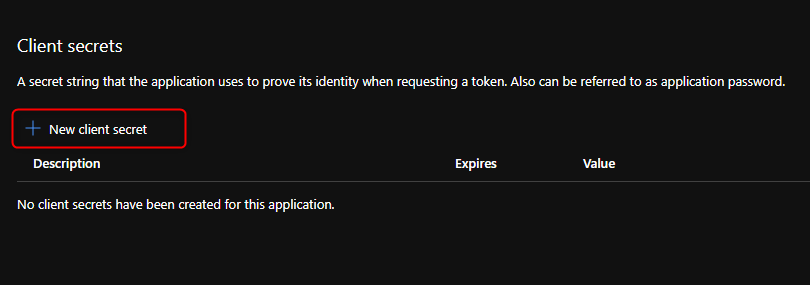
Enter a unique description, select the duration of the secret.
Click on Add
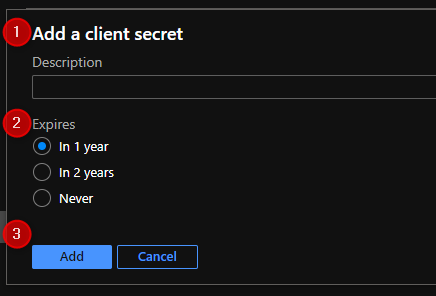
Copy the secret string. Keep it and save it with the Application and Directory ID.
Step 4 – Giving the Proper Permissions
Using an App registration gives you the ability to connect to your client’s environments and generate documentation for them securely.
You will be able to set scheduled document generation for your different customers and run everything in an automated fashion. From scheduling all the way to dropping the information in one of your customer’s storage account.
GIVING PERMISSIONS TO THE APPLICATION ON THE SUBSCRIPTION
Privilege requirements to gather information from the cloud provider’s public APIs is “Reading”.
Access the subscription you want to give access to.
Click on the subscription name and select Access Control (IAM)

Click on the Add button in the Add a role assignment box.
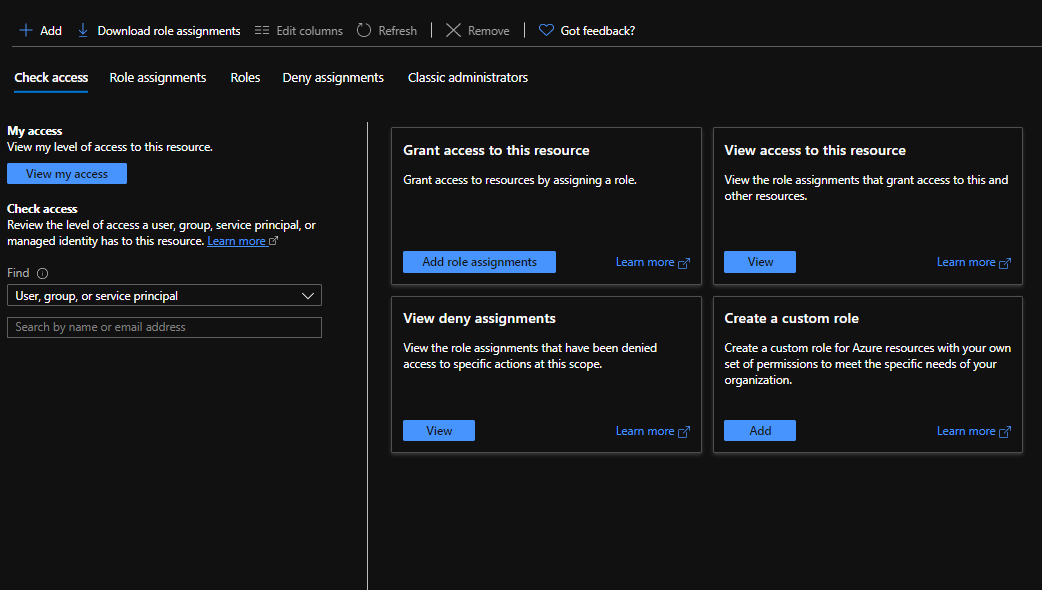
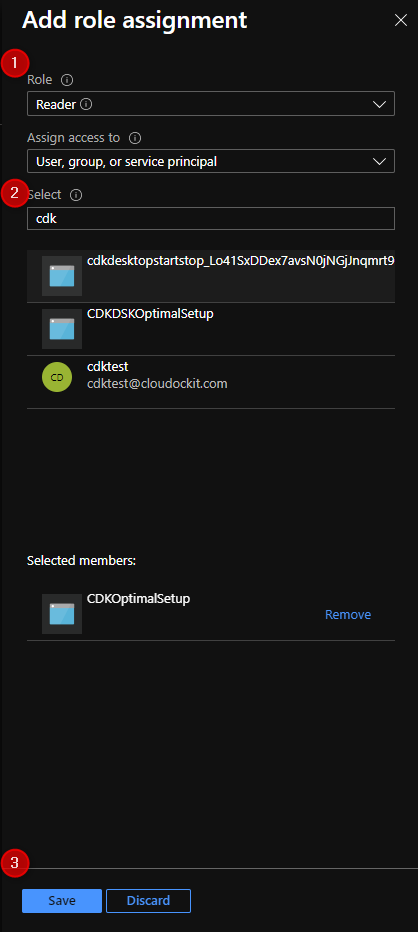
In the Add a role assignment section, select the following:
- Role: Reader
- Select the Application you have created.
Make sure the application is in the Selected members’ section.
Click on Save
GIVING THE APPLICATION PERMISSIONS ON THE STORAGE ACCOUNT
Access the list of storage accounts in your subscription and select the one where you want to drop off your documents from Cloudockit Desktop.
Click on Access Control (IAM)
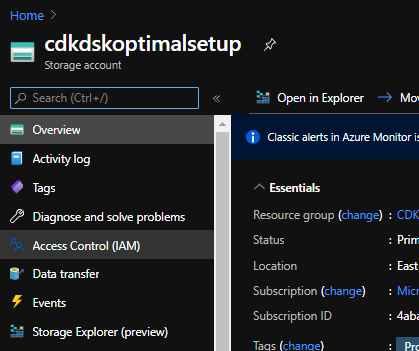
Click on the Add button in the Add a role assignment box.
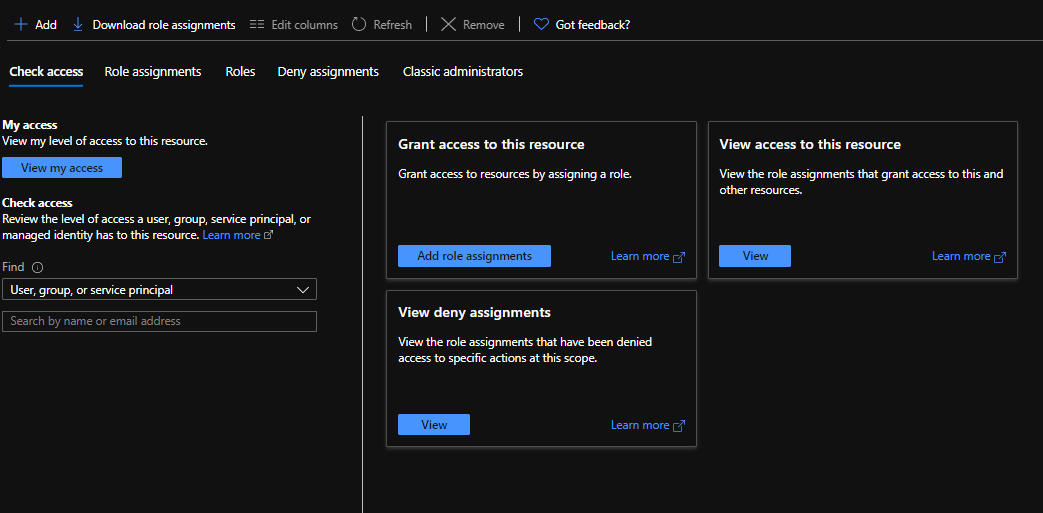
In the Add a role assignment section, select the following:
- Role: Reader and Data Access
- Select: Select the virtual machine you created
Make sure the Virtual machine is in the Selected members’ section.
Click on Save
ADDITIONAL PERMISSIONS
Azure Classic Resources
Classic resources will not display in the documentation with reader privileges.
You must add the credentials to the “Classic Administrator” of the subscription.
Documentation for Role-Based Access Control.
Azure Active Directory
Cloudockit cannot retrieve data from Azure Directory with reader privileges.
The credentials used to generate the documentation must have “Azure AD Global Administrator”.
Azure Billing
Limited billing information can be retrieved with reader privileges. To get access to additional billing information you must give the credentials “Billing Reader” privileges.
Azure Security Center
To read information from the Azure Security Center through the compliance rules, the credentials used to generate the documentation must have “Security Reader” privileges.
Dependency Detection in Azure App Services
Cloudockit automatically detects dependencies between components like Azure App Services & Functions and components like storages, queues, etc.
To do that, Cloudockit scans the App Settings and App Connection Strings to detect the components the App Service is communicating with.
Contributor access (on the App Service only) is needed to allow Cloudockit to list the App Settings and Connection Strings. If you have only Reader privileges, you will see the App Service Details but not the dependencies.
Azure Kubernetes Services
The credentials used to generate the documentation must have Azure Kubernetes Service RBAC Writer access (on the Kubernetes Cluster only) to allow Cloudockit to connect to the cluster and retrieve the details.
Step 5 – Launch Cloudockit Desktop and Schedule a Document Generation
Connect to the Virtual Machine just created.
CREATE A SHORTCUT
The first step is to create a shortcut to launch Cloudockit from your desktop.
Open Windows Explorer and go to this folder, C:\Program Files\CloudocKit
Identify the file named Cloudockit.exe
Create a shortcut and place it on your desktop.
ACTIVATING CLOUDOCKIT
Click on the desktop shortcut of Cloudockit to launch the application.
You will need to enter your product key to activate Cloudockit Desktop.
If you have not purchased a product key yet, please visit our Pricing Page.
You will see a message confirming that the activation was done successfully.

Click: OK
CONNECTING TO AN AZURE PLATFORM
Click on Start or Schedule a document generation.
Select Microsoft Azure from the list of platforms.

Select Managed Identity (Preview).
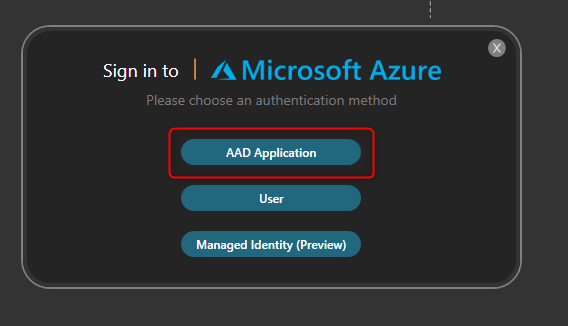
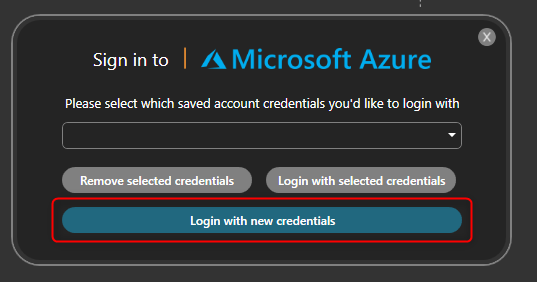
Click on Login with new credentials.
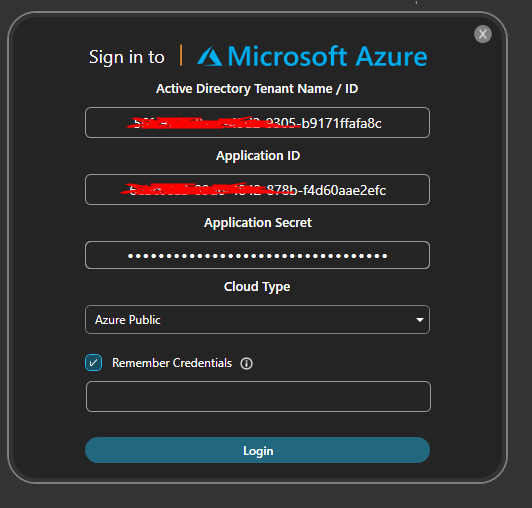
Enter the Directory ID, Application ID, and Application secret.
You can also check the Remember Credentials box and give these credentials a unique name to access them quickly next time around.
Click on Login
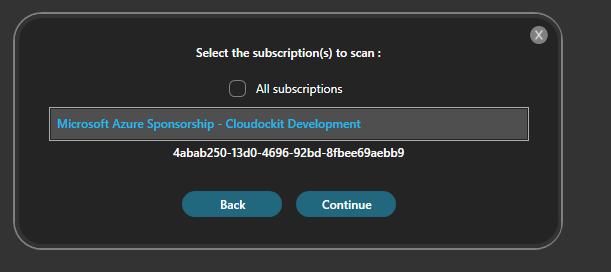
Select the subscription(s) you want to document, and click on Continue.
SCHEDULE A DOCUMENT GENERATION
Now that you are logged in, it is time to define what information you want to generate using Cloudockit.
Set the desired parameters under Documents, Workloads, and Organize Content.
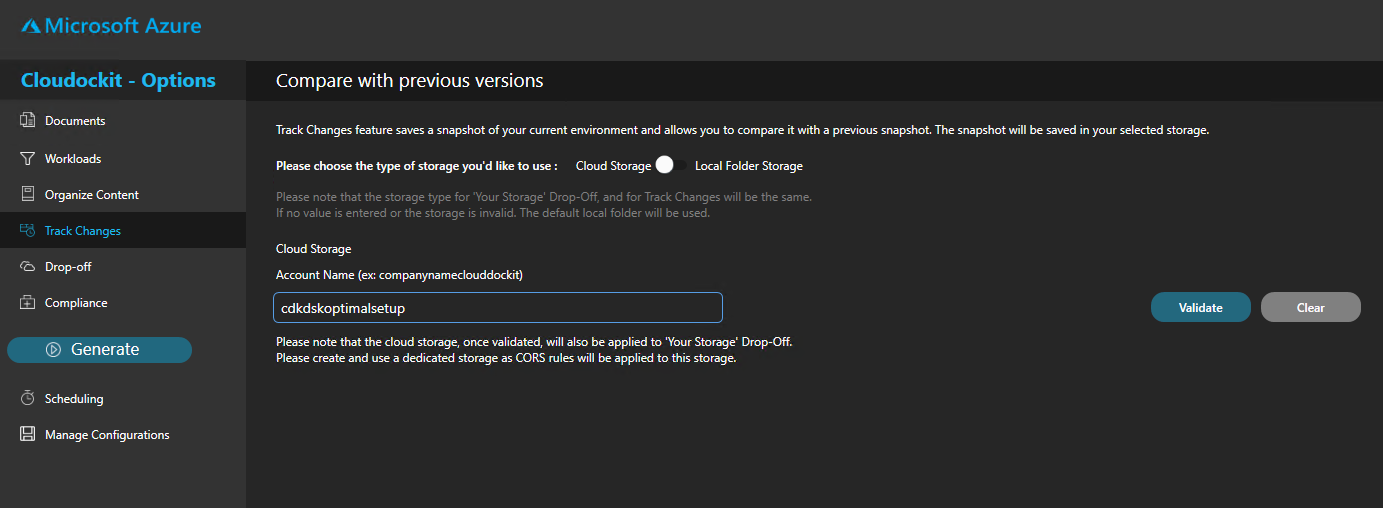
TRACK CHANGES
Use the storage account created previously to track changes. This will allow you to see the differences that have occurred between a previous document and the one running right now.
Select Track Changes from the menu to the left.
Enter the name of the storage account in the Account Name box and press validate.
A confirmation message will confirm that the storage account is valid.
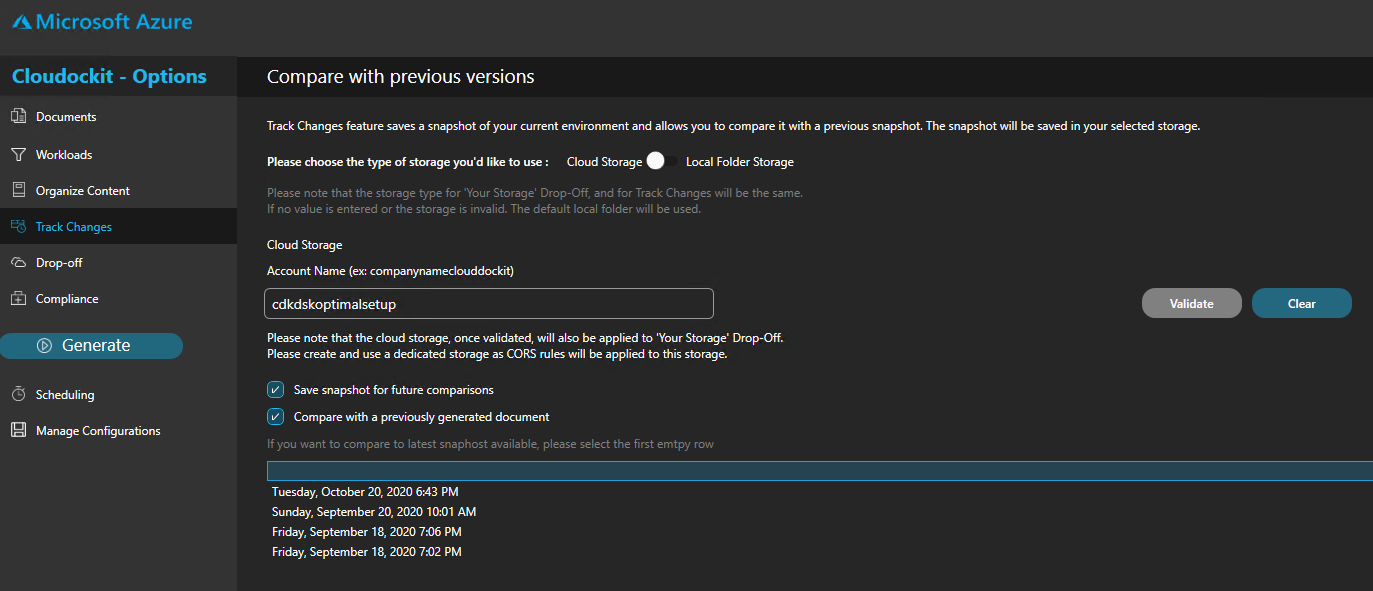
Check the box Save a snapshot for comparison.
This will save a JSON file in the storage account every time a new document is generated.
Check the box Compare with a previously generated document.
Select the first empty row that appears below.
This will always select the most recent file in the storage account to compare.
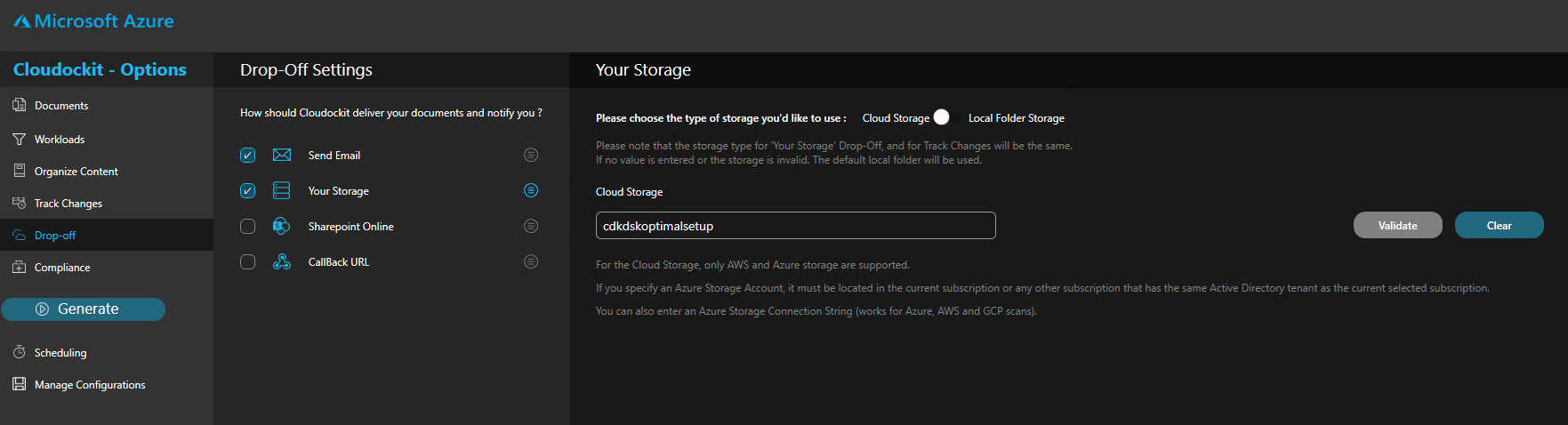
DROP-OFF
In the Drop-off settings, the same storage account as defined in the Track Changes section is automatically selected.
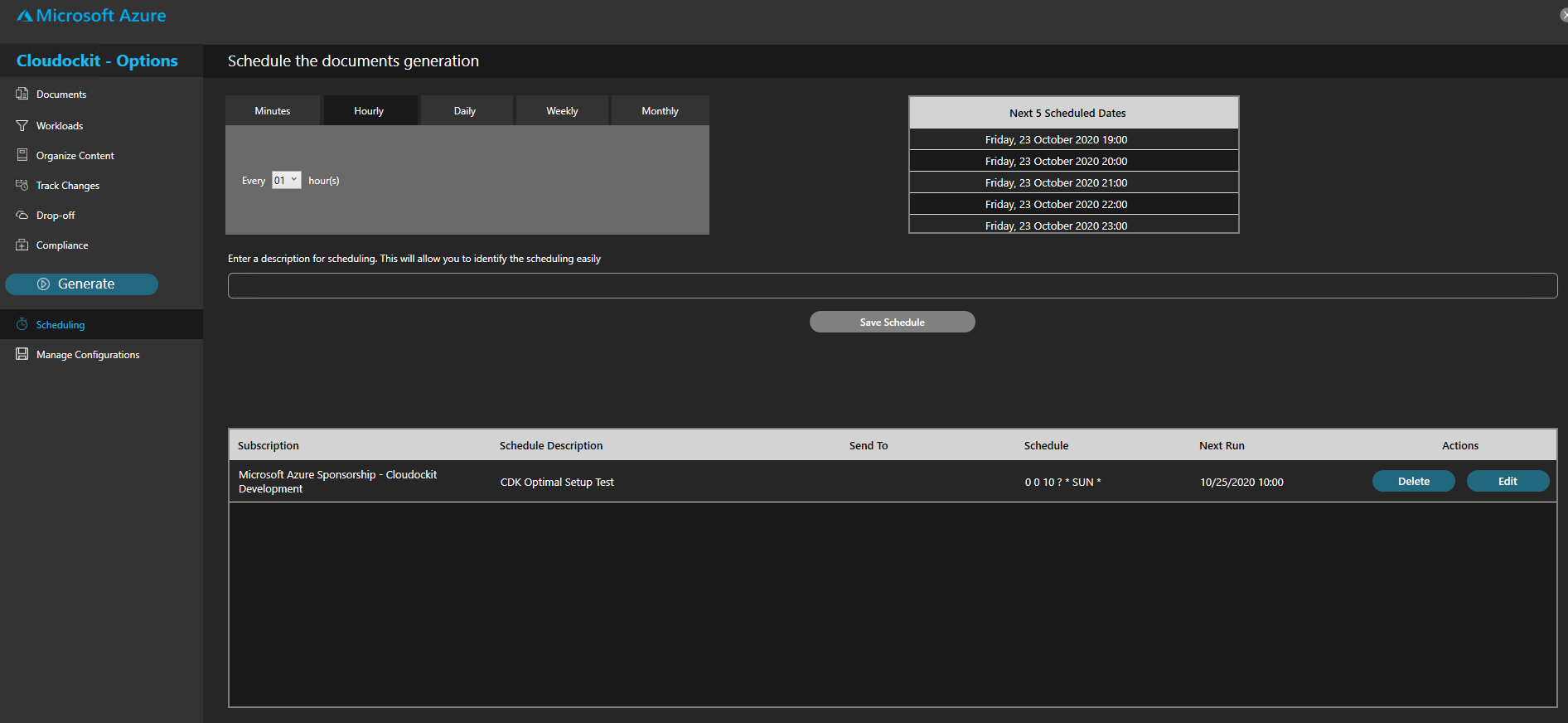
SCHEDULING
Define the desired schedule for your documentation to run and save your schedule.
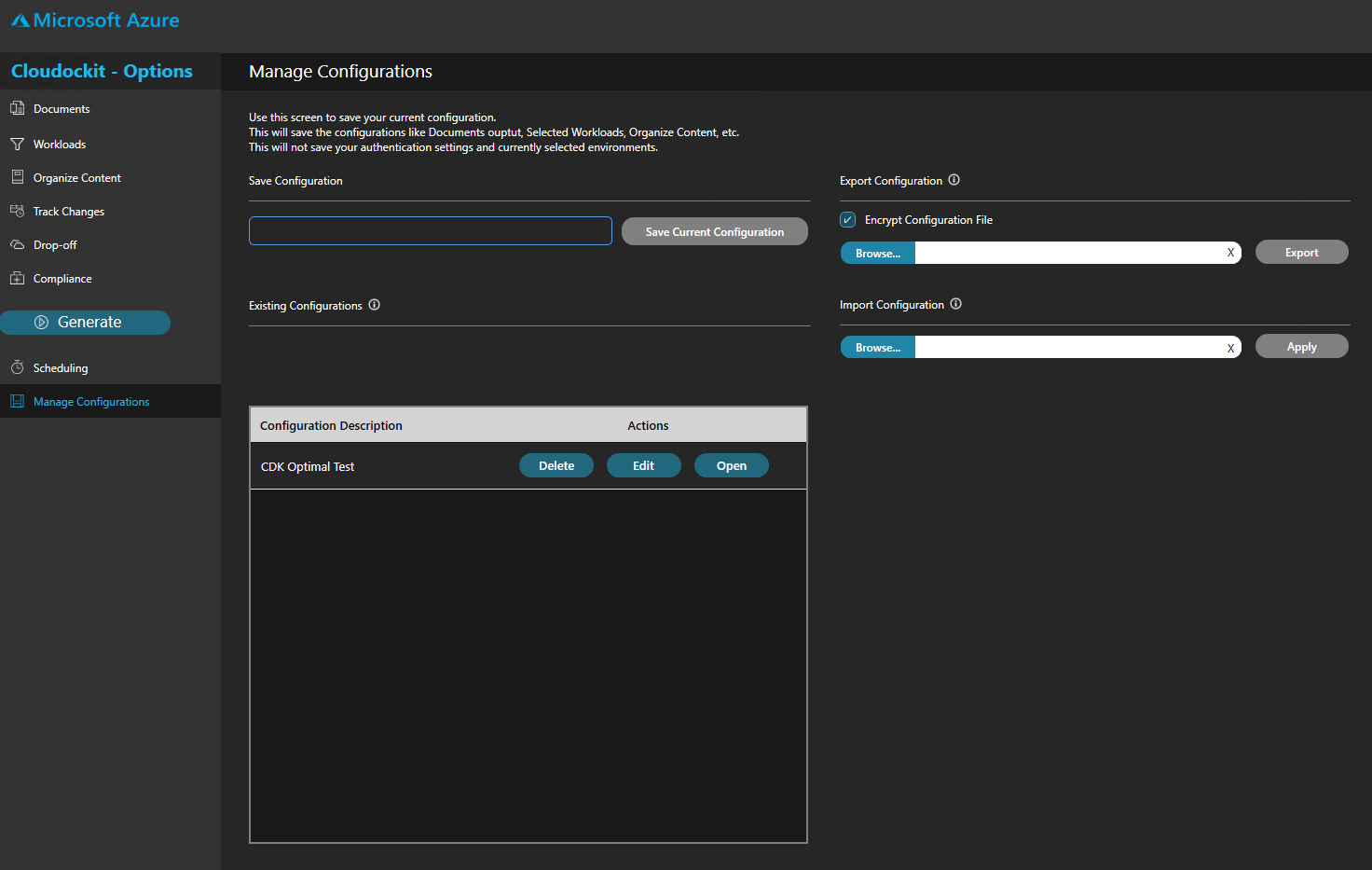
CONFIGURATION
Enter a unique name to the parameters you have set and click on Save Current Configuration.
Your configuration is saved, you can load or edit it in the future.
Step 6 – Validate that Documents are Successfully Generated
Once your scheduled document generation is complete, let’s validate that it has been scheduled properly.
From the main menu, select View all schedules.
In the list, you will see the scheduled documentation you have configured.
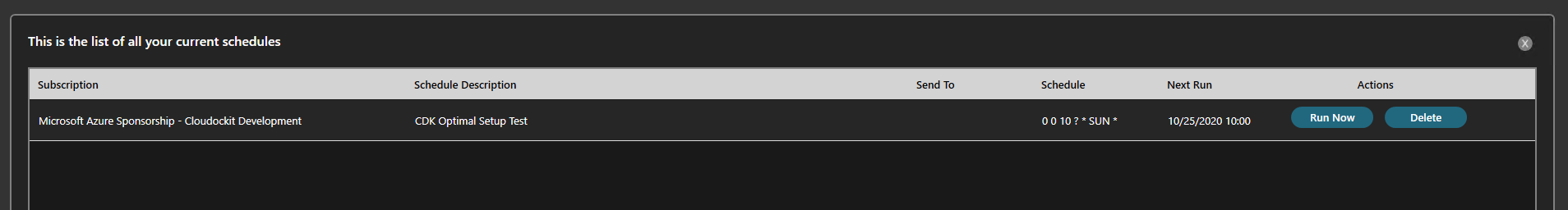
You can now press run to generate a manual document generation or wait for the schedule to run its course.
Once your document is completed, you will be able to access it from the Storage Account or from the desktop application.
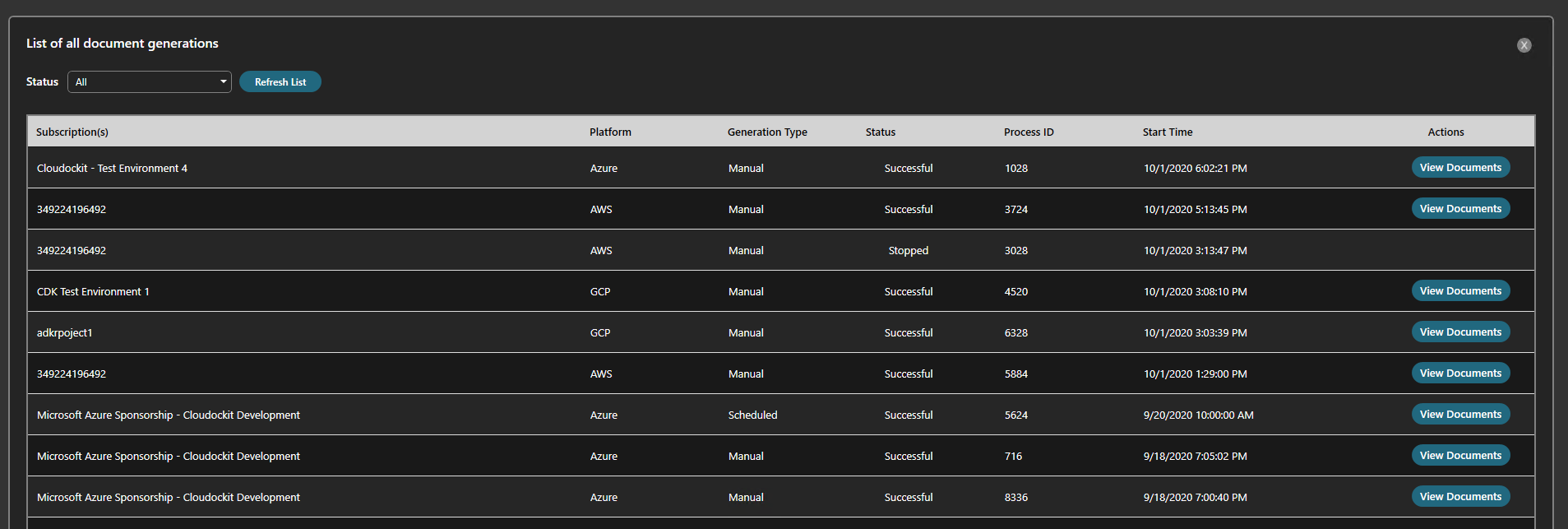
Click on View all document generations from the main menu.
You will see the list of the documents that have been generated.
You can access the documents from the View Documents button on the right.